“The Event Flow”的版本间的差异
(→stopPropagation與stopImmediatePropagation的區別) |
|||
| (未显示同一用户的38个中间版本) | |||
| 第4行: | 第4行: | ||
==事件流機制圖示== | ==事件流機制圖示== | ||
<center>[[Image:FlashPlatform_EFA.jpg]]</center><br/> | <center>[[Image:FlashPlatform_EFA.jpg]]</center><br/> | ||
| + | 从概念上来讲事件流分成了三个部分: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:FlashPlatform_Numbers1.jpg]]捕獲階段: 此階段包括從舞台到發送事件的目標對象的父節點間的所有節點。 | ||
| + | [[Image:FlashPlatform_Numbers2.jpg]]目標階段: 此階段只包括發送事件的目標對象節點。 | ||
| + | [[Image:FlashPlatform_Numbers3.jpg]]冒泡階段: 此階段包含的階段和捕獲階段相同,但此階段事件傳遞方向和捕獲階段剛好相反。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | 一個事件必須經過EventDispatcher派發出來。 | ||
| + | 根據DOM Tree定義。找到目標對象在DOM Tree中的定義並獲得此節點到DOM tree根節點的單根路徑。 | ||
| + | 因此一個非顯示對象只能參與[[Image:FlashPlatform_Numbers2.jpg]]階段。因為一個沒有表象的非顯示對象在DOM中不存在父節點。 | ||
| + | 而對於顯示對象通常都能有父顯示容器。因此在DOM Tree中通常可以找到父節點的定義。 | ||
| + | 只有一種情況下例外,當一個顯示物件不包含任何子顯示元素同時沒有被加入到Display list(顯示列表)中。 | ||
| + | 此是這個顯示對象和非顯示對象的一樣只能參與[[Image:FlashPlatform_Numbers2.jpg]]階段。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
==用這個圖所示結構來說明ActionScript3事件流機制== | ==用這個圖所示結構來說明ActionScript3事件流機制== | ||
<center>[[Image:FlashPlatform_EF.jpg]]</center><br/> | <center>[[Image:FlashPlatform_EF.jpg]]</center><br/> | ||
| 第10行: | 第24行: | ||
==實現圖示結構的代碼== | ==實現圖示結構的代碼== | ||
這個例子用於創建如上圖中所示的結構。<br/> | 這個例子用於創建如上圖中所示的結構。<br/> | ||
| − | 我們為A,B,C1, | + | 我們為A,B,C1,C2分別加入了所有階段監聽。 |
<syntaxhighlight lang="actionscript"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="actionscript"> | ||
package { | package { | ||
| 第33行: | 第47行: | ||
stage.addChild(A); | stage.addChild(A); | ||
// add event listeners | // add event listeners | ||
| − | A.addEventListener("myEvent", | + | A.addEventListener("myEvent", A_listener1, true); |
| − | B.addEventListener("myEvent", B_listener1); | + | A.addEventListener("myEvent", A_listener2); |
| + | B.addEventListener("myEvent", B_listener1, true); | ||
B.addEventListener("myEvent", B_listener2); | B.addEventListener("myEvent", B_listener2); | ||
| − | C1.addEventListener("myEvent", | + | C1.addEventListener("myEvent", C1_listener1, true); |
| − | C1.addEventListener("myEvent", | + | C1.addEventListener("myEvent", C1_listener2); |
| + | C2.addEventListener("myEvent", C2_listener1, true); | ||
| + | C2.addEventListener("myEvent", C2_listener2); | ||
// dispatch event | // dispatch event | ||
// ${1} | // ${1} | ||
| 第44行: | 第61行: | ||
// Event listeners | // Event listeners | ||
//========================================================================== | //========================================================================== | ||
| − | private function | + | private function A_listener1(event:Event):void { |
| + | trace("A處捕獲(非冒泡階段)"); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | private function A_listener2(event:Event):void { | ||
trace("A處捕獲"); | trace("A處捕獲"); | ||
} | } | ||
private function B_listener1(event:Event):void { | private function B_listener1(event:Event):void { | ||
| − | trace("B處捕獲( | + | trace("B處捕獲(非冒泡階段)"); |
} | } | ||
private function B_listener2(event:Event):void { | private function B_listener2(event:Event):void { | ||
trace("B處捕獲"); | trace("B處捕獲"); | ||
} | } | ||
| − | private function | + | private function C1_listener1(event:Event):void { |
| + | trace("C1處捕獲(非冒泡階段)"); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | private function C1_listener2(event:Event):void { | ||
trace("C1處捕獲"); | trace("C1處捕獲"); | ||
} | } | ||
| − | private function | + | private function C2_listener1(event:Event):void { |
| + | trace("C2處捕獲(非冒泡階段)"); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | private function C2_listener2(event:Event):void { | ||
trace("C2處捕獲"); | trace("C2處捕獲"); | ||
} | } | ||
| 第62行: | 第88行: | ||
} | } | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==基本的事件發送和捕獲== | ||
| + | ${1}處加入以下代碼 | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="actionscript"> | ||
| + | C1.dispatchEvent(new Event("myEvent")); | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | 會看到以下輸出。 | ||
| + | A處捕獲(非冒泡階段) | ||
| + | B處捕獲(非冒泡階段) | ||
| + | C1處捕獲 | ||
| + | 這個圖可以解釋以上結果。 | ||
| + | <center>[[Image:FlashPlatform EFTEST1.jpg]]</center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==打開事件的冒泡會如何== | ||
| + | ${1}處代碼改為 | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="actionscript"> | ||
| + | C1.dispatchEvent(new Event("myEvent")); | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 會看到如下輸出。 | ||
| + | A處捕獲(非冒泡階段) | ||
| + | B處捕獲(非冒泡階段) | ||
| + | C1處捕獲 | ||
| + | B處捕獲 | ||
| + | A處捕獲 | ||
| + | |||
| + | 這個圖可以解釋以上結果。 | ||
| + | <center>[[Image:FlashPlatform EFTEST2.jpg]]</center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 你可能會奇怪為甚麼C2_listener1函數並沒有執行。 | ||
| + | 其實這個函數的存在是多餘的。因為這個監聽的useCapture為true | ||
| + | IEventDispatcher.addEventListener方法的useCapture說明為 | ||
| + | 判斷偵聽程式是否可在捕捉階段或目標與反昇階段運作。 如果 useCapture 設為 true,則偵聽程式只會在捕捉階段 (而不是在目標或反昇階段) 處理事件。 | ||
| + | 如果 useCapture 為 false,則偵聽程式只會在目標或反昇階段處理事件。 若要在全部三個階段中偵聽事件,請呼叫 addEventListener 兩次, | ||
| + | 先將 useCapture 設為 true 後進行第一次呼叫,接著將 useCapture 設為 false 再進行第二次呼叫。 | ||
| + | 我們可以圖示來簡單說明為甚麼這個監聽沒起任何作用。 | ||
| + | <center>[[Image:FlashPlatform EFTEST3.jpg]]</center> | ||
| + | 如圖所示因為這個函數士這樣加入的。 | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="actionscript"> | ||
| + | C1.addEventListener("myEvent", C1_listener1, true); | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | 因此它無法參與[[Image:FlashPlatform_Numbers2.jpg]]目標階段和[[Image:FlashPlatform_Numbers3.jpg]]冒泡階段。 | ||
| + | 然而這個監聽又是加在C1節點上。即[[Image:FlashPlatform_Numbers2.jpg]]目標節點物體。因此它起不到作用。 | ||
| + | ==自定義事件== | ||
| + | 事件實質上是一種VO(Value Object) | ||
| + | 所以推薦事件對象的屬性多使用只讀屬性。 | ||
| + | 創建起來很簡單。'''(注意常量定義單詞用_分開,賦值以小寫開頭每個單詞首字大寫,舞分隔符)''' | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="actionscript"> | ||
| + | package events { | ||
| + | import flash.events.Event; | ||
| + | |||
| + | public class CustomEvent extends Event { | ||
| + | // ${1} | ||
| + | public static const MY_EVENT_TYPE:String = "myEventType"; | ||
| + | /** Constructor */ | ||
| + | public function CustomEvent(type:String, bubbles:Boolean = false, | ||
| + | cancelable:Boolean = false) { | ||
| + | super(type, bubbles, cancelable); | ||
| + | $data = {}; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | private var $data:Object; | ||
| + | public function get data():Object { | ||
| + | return $data; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } // <- end class -> | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 為了規範。也為了使用自定義事件可以更方便得知一個事件的作用。可以在${1}處加上註釋。 | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="actionscript"> | ||
| + | /** | ||
| + | * 這個是字定義事件類型的描述。 | ||
| + | * <p>此事件具有以下屬性值:</p> | ||
| + | * <table class="innertable"> | ||
| + | * <tr><th>屬性名稱</th><th>值</th></tr> | ||
| + | * <tr><td><code>bubbles</code></td><td>false</td></tr> | ||
| + | * <tr><td><code>cancelable</code></td><td>false</td></tr> | ||
| + | * <tr><td><code>data</code></td><td>帶有用戶參數</td></tr> | ||
| + | * </table> | ||
| + | * @eventType myEventType | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | 這樣你可以得到一個很漂亮的asdoc檔<br/> | ||
| + | <center>[[Image:FlashPlatform_EFTEST5.png]]</center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 如果是使用的Flash Builder開發。那麼以下內容可以讓事件更容易使用。<br/> | ||
| + | 你可以在將拋出此時間的特定類中聲名此事件。 | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="actionscript"> | ||
| + | package { | ||
| + | import flash.events.EventDispatcher; | ||
| + | /** | ||
| + | * @eventType events.CustomEvent.MY_EVENT_TYPE | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | [Event(name="myEventType", type="events.CustomEvent")] | ||
| + | public class MyEventDispatcher extends EventDispatcher { | ||
| + | /** Constructor */ | ||
| + | public function MyEventDispatcher() { | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } // <- end class -> | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | 這樣在您調度此類的實例的addEventListener方法時,這個事件會自動列出。 | ||
| + | <center>[[Image:FlashPlatform EFTEST4.png]]</center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==如何創建事件的默認阻止行為== | ||
| + | 我們給上面的MyEventDispatcher類加上一個方法'''注意第3個參數必須是true''' | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="actionscript"> | ||
| + | public function say():void { | ||
| + | const SUCCESS:Boolean = dispatchEvent(new CustomEvent(CustomEvent.MY_EVENT_TYPE, false, true)); | ||
| + | if(!SUCCESS) | ||
| + | return; | ||
| + | trace("雷神也有春天"); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | 這就是一個可阻止的事件派發機制。我們經常用到監聽TextEvent.TEXT_INPUT並在輸入一些我們不允許的字符時返回,也是使用這種方式。<br/> | ||
| + | 接下來可以測試這段代碼是如何工作的。<br/> | ||
| + | 我們在創建一個MyEventDispatcher對象並監聽自定義事件。 | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="actionscript"> | ||
| + | const MED:MyEventDispatcher = new MyEventDispatcher(); | ||
| + | MED.addEventListener(CustomEvent.MY_EVENT_TYPE, eventHandler); | ||
| + | function eventHandler(event:Event):void { | ||
| + | // ${2} | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | MED.say(); | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | 會得到以下輸出 | ||
| + | 雷神也有春天 | ||
| + | 現在在${2}處加入代碼 | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="actionscript"> | ||
| + | event.preventDefault(); | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | 於是就得不到任何的輸出了。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==stopPropagation與stopImmediatePropagation的區別== | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="actionscript"> | ||
| + | package { | ||
| + | import flash.display.Sprite; | ||
| + | import flash.events.Event; | ||
| + | |||
| + | public class Test extends Sprite { | ||
| + | //========================================================================== | ||
| + | // Constructor | ||
| + | //========================================================================== | ||
| + | /** Constructor */ | ||
| + | public function Test() { | ||
| + | const A:Sprite = new Sprite(); | ||
| + | const B:Sprite = new Sprite(); | ||
| + | A.addChild(B); | ||
| + | addChild(A); | ||
| + | |||
| + | A.addEventListener("myEvent", A_listener1, true); | ||
| + | A.addEventListener("myEvent", A_listener2, true); | ||
| + | B.addEventListener("myEvent", B_listener); | ||
| + | B.dispatchEvent(new Event("myEvent")); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | //========================================================================== | ||
| + | // Event listeners | ||
| + | //========================================================================== | ||
| + | private function A_listener1(event:Event):void { | ||
| + | trace("A_listener1"); | ||
| + | // ${1} | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | private function A_listener2(event:Event):void { | ||
| + | trace("A_listener2"); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | private function B_listener(event:Event):void { | ||
| + | trace("B_listener"); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } // <- end class -> | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | 得到以下輸出 | ||
| + | A_listener1 | ||
| + | A_listener2 | ||
| + | B_listener | ||
| + | 在${1}處加入代碼 | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="actionscript"> | ||
| + | event.stopPropagation(); | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | 得到以下輸出。後續節點的事件監聽被中斷了。<br/> | ||
| + | A_listener1 | ||
| + | A_listener2 | ||
| + | 如果修改${1}代碼為 | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="actionscript"> | ||
| + | event.stopImmediatePropagation(); | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | 得到以下輸出 | ||
| + | A_listener1 | ||
| + | 那麼當前節點的優先級小於A_listener1的監聽函數也會被中斷。意義上的不許動,全部給我停下來。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | === 參考資料 === | ||
| + | *[http://www.w3.org/DOM/ W3C DOM] | ||
2011-04-15T09:27:37的最后版本
關於 ActionScript3 事件流。
目录
事件流機制圖示
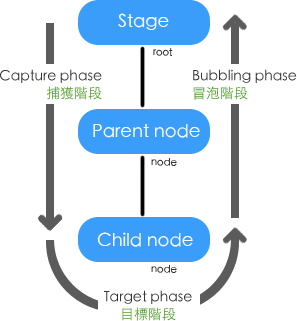
从概念上来讲事件流分成了三个部分:捕獲階段: 此階段包括從舞台到發送事件的目標對象的父節點間的所有節點。
目標階段: 此階段只包括發送事件的目標對象節點。
冒泡階段: 此階段包含的階段和捕獲階段相同,但此階段事件傳遞方向和捕獲階段剛好相反。 一個事件必須經過EventDispatcher派發出來。 根據DOM Tree定義。找到目標對象在DOM Tree中的定義並獲得此節點到DOM tree根節點的單根路徑。 因此一個非顯示對象只能參與
階段。因為一個沒有表象的非顯示對象在DOM中不存在父節點。 而對於顯示對象通常都能有父顯示容器。因此在DOM Tree中通常可以找到父節點的定義。 只有一種情況下例外,當一個顯示物件不包含任何子顯示元素同時沒有被加入到Display list(顯示列表)中。 此是這個顯示對象和非顯示對象的一樣只能參與
階段。
用這個圖所示結構來說明ActionScript3事件流機制
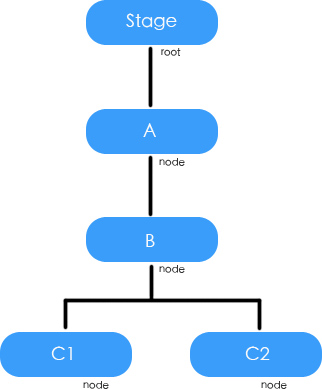
實現圖示結構的代碼
這個例子用於創建如上圖中所示的結構。
我們為A,B,C1,C2分別加入了所有階段監聽。
package { import flash.display.Sprite; import flash.display.StageAlign; import flash.display.StageScaleMode; import flash.events.Event; public class Test extends Sprite { //========================================================================== // Constructor //========================================================================== /** Constructor */ public function Test() { // init const A:Sprite = new Sprite(); const B:Sprite = new Sprite(); const C1:Sprite = new Sprite(); const C2:Sprite = new Sprite(); B.addChild(C1); B.addChild(C2); A.addChild(B); stage.addChild(A); // add event listeners A.addEventListener("myEvent", A_listener1, true); A.addEventListener("myEvent", A_listener2); B.addEventListener("myEvent", B_listener1, true); B.addEventListener("myEvent", B_listener2); C1.addEventListener("myEvent", C1_listener1, true); C1.addEventListener("myEvent", C1_listener2); C2.addEventListener("myEvent", C2_listener1, true); C2.addEventListener("myEvent", C2_listener2); // dispatch event // ${1} } //========================================================================== // Event listeners //========================================================================== private function A_listener1(event:Event):void { trace("A處捕獲(非冒泡階段)"); } private function A_listener2(event:Event):void { trace("A處捕獲"); } private function B_listener1(event:Event):void { trace("B處捕獲(非冒泡階段)"); } private function B_listener2(event:Event):void { trace("B處捕獲"); } private function C1_listener1(event:Event):void { trace("C1處捕獲(非冒泡階段)"); } private function C1_listener2(event:Event):void { trace("C1處捕獲"); } private function C2_listener1(event:Event):void { trace("C2處捕獲(非冒泡階段)"); } private function C2_listener2(event:Event):void { trace("C2處捕獲"); } } // <- end class -> }
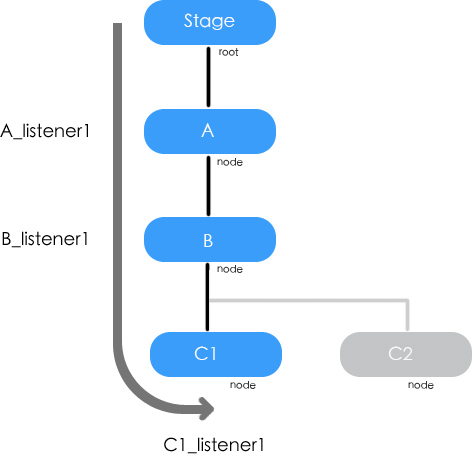
基本的事件發送和捕獲
${1}處加入以下代碼
C1.dispatchEvent(new Event("myEvent"));
會看到以下輸出。
A處捕獲(非冒泡階段) B處捕獲(非冒泡階段) C1處捕獲
這個圖可以解釋以上結果。
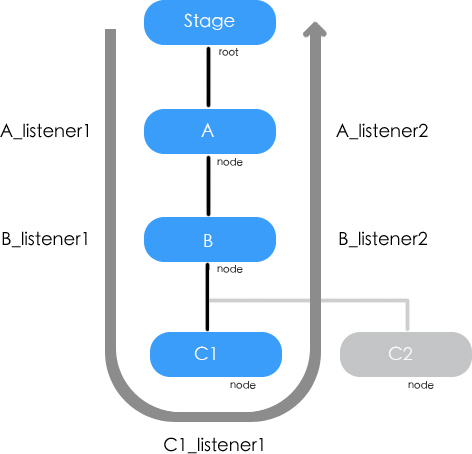
打開事件的冒泡會如何
${1}處代碼改為
C1.dispatchEvent(new Event("myEvent"));
會看到如下輸出。
A處捕獲(非冒泡階段) B處捕獲(非冒泡階段) C1處捕獲 B處捕獲 A處捕獲
這個圖可以解釋以上結果。
你可能會奇怪為甚麼C2_listener1函數並沒有執行。 其實這個函數的存在是多餘的。因為這個監聽的useCapture為true IEventDispatcher.addEventListener方法的useCapture說明為 判斷偵聽程式是否可在捕捉階段或目標與反昇階段運作。 如果 useCapture 設為 true,則偵聽程式只會在捕捉階段 (而不是在目標或反昇階段) 處理事件。 如果 useCapture 為 false,則偵聽程式只會在目標或反昇階段處理事件。 若要在全部三個階段中偵聽事件,請呼叫 addEventListener 兩次, 先將 useCapture 設為 true 後進行第一次呼叫,接著將 useCapture 設為 false 再進行第二次呼叫。 我們可以圖示來簡單說明為甚麼這個監聽沒起任何作用。
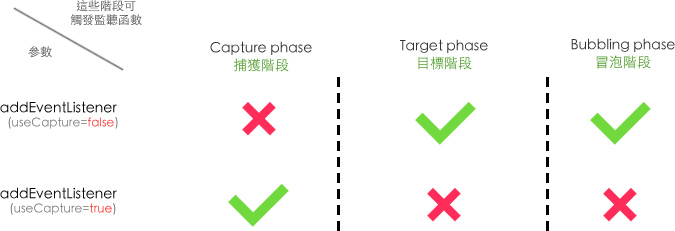
如圖所示因為這個函數士這樣加入的。
C1.addEventListener("myEvent", C1_listener1, true);
因此它無法參與![]() 目標階段和
目標階段和![]() 冒泡階段。
然而這個監聽又是加在C1節點上。即
冒泡階段。
然而這個監聽又是加在C1節點上。即![]() 目標節點物體。因此它起不到作用。
目標節點物體。因此它起不到作用。
自定義事件
事件實質上是一種VO(Value Object) 所以推薦事件對象的屬性多使用只讀屬性。 創建起來很簡單。(注意常量定義單詞用_分開,賦值以小寫開頭每個單詞首字大寫,舞分隔符)
package events { import flash.events.Event; public class CustomEvent extends Event { // ${1} public static const MY_EVENT_TYPE:String = "myEventType"; /** Constructor */ public function CustomEvent(type:String, bubbles:Boolean = false, cancelable:Boolean = false) { super(type, bubbles, cancelable); $data = {}; } private var $data:Object; public function get data():Object { return $data; } } // <- end class -> }
為了規範。也為了使用自定義事件可以更方便得知一個事件的作用。可以在${1}處加上註釋。
/**
* 這個是字定義事件類型的描述。
* <p>此事件具有以下屬性值:</p>
* <table class="innertable">
* <tr><th>屬性名稱</th><th>值</th></tr>
* <tr><td><code>bubbles</code></td><td>false</td></tr>
* <tr><td><code>cancelable</code></td><td>false</td></tr>
* <tr><td><code>data</code></td><td>帶有用戶參數</td></tr>
* </table>
* @eventType myEventType
*/這樣你可以得到一個很漂亮的asdoc檔

如果是使用的Flash Builder開發。那麼以下內容可以讓事件更容易使用。
你可以在將拋出此時間的特定類中聲名此事件。
package { import flash.events.EventDispatcher; /** * @eventType events.CustomEvent.MY_EVENT_TYPE */ [Event(name="myEventType", type="events.CustomEvent")] public class MyEventDispatcher extends EventDispatcher { /** Constructor */ public function MyEventDispatcher() { } } // <- end class -> }
這樣在您調度此類的實例的addEventListener方法時,這個事件會自動列出。
如何創建事件的默認阻止行為
我們給上面的MyEventDispatcher類加上一個方法注意第3個參數必須是true
public function say():void { const SUCCESS:Boolean = dispatchEvent(new CustomEvent(CustomEvent.MY_EVENT_TYPE, false, true)); if(!SUCCESS) return; trace("雷神也有春天"); }
這就是一個可阻止的事件派發機制。我們經常用到監聽TextEvent.TEXT_INPUT並在輸入一些我們不允許的字符時返回,也是使用這種方式。
接下來可以測試這段代碼是如何工作的。
我們在創建一個MyEventDispatcher對象並監聽自定義事件。
const MED:MyEventDispatcher = new MyEventDispatcher(); MED.addEventListener(CustomEvent.MY_EVENT_TYPE, eventHandler); function eventHandler(event:Event):void { // ${2} } MED.say();
會得到以下輸出
雷神也有春天
現在在${2}處加入代碼
event.preventDefault();
於是就得不到任何的輸出了。
stopPropagation與stopImmediatePropagation的區別
package { import flash.display.Sprite; import flash.events.Event; public class Test extends Sprite { //========================================================================== // Constructor //========================================================================== /** Constructor */ public function Test() { const A:Sprite = new Sprite(); const B:Sprite = new Sprite(); A.addChild(B); addChild(A); A.addEventListener("myEvent", A_listener1, true); A.addEventListener("myEvent", A_listener2, true); B.addEventListener("myEvent", B_listener); B.dispatchEvent(new Event("myEvent")); } //========================================================================== // Event listeners //========================================================================== private function A_listener1(event:Event):void { trace("A_listener1"); // ${1} } private function A_listener2(event:Event):void { trace("A_listener2"); } private function B_listener(event:Event):void { trace("B_listener"); } } // <- end class -> }
得到以下輸出
A_listener1 A_listener2 B_listener
在${1}處加入代碼
event.stopPropagation();
得到以下輸出。後續節點的事件監聽被中斷了。
A_listener1 A_listener2
如果修改${1}代碼為
event.stopImmediatePropagation();
得到以下輸出
A_listener1
那麼當前節點的優先級小於A_listener1的監聽函數也會被中斷。意義上的不許動,全部給我停下來。